템플릿 메서드 패턴이란 여러 클래스에서 공통으로 사용하는 메서드(변하지 않는 기능)를 템플릿이라는 상위 클래스에 정의하고 세부 동작을 하위 클래스에서 구현하도록 하는 패턴이다.
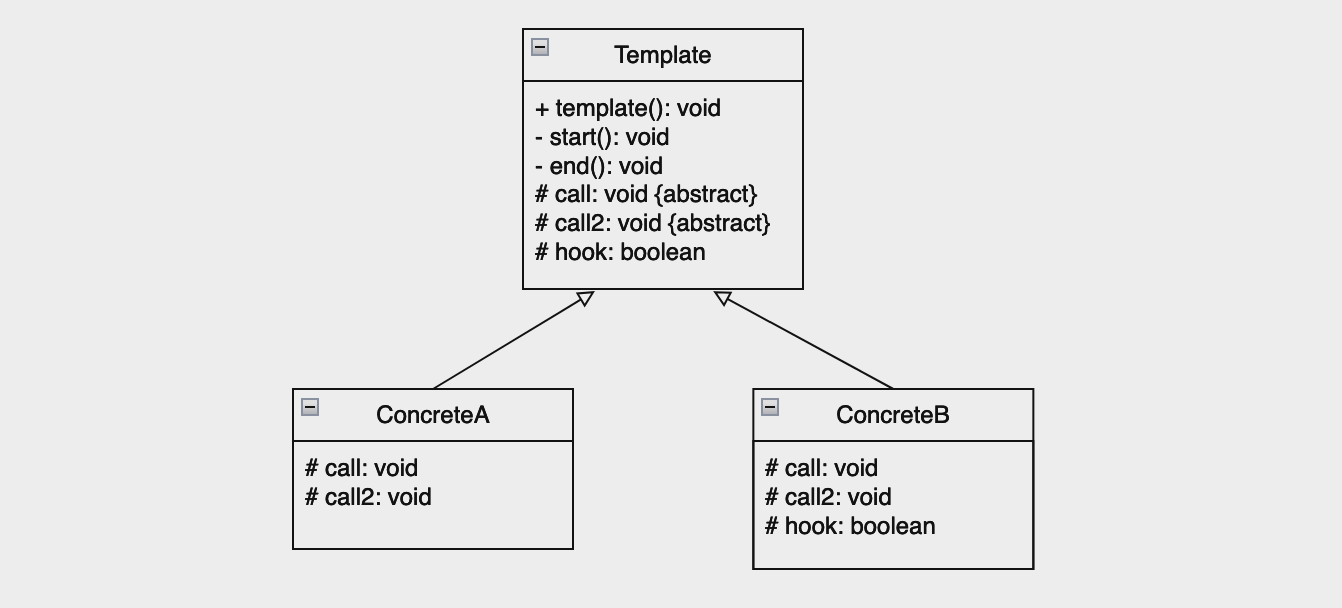
- Abstract Class (추상 클래스)
- 알고리즘의 구조(템플릿 메서드)를 정의
- 공통적으로 처리하는 일부 메서드는 구현하며, 나머지는 추상 메서드로 선언되어 하위 클래스에서 구현
- Concrete Class (구체 클래스)
- 상위 클래스에서 정의된 추상 메서드를 구현
- 구현한 메서드는 상위 클래스에서 제공하는 템플릿 메서드를 통해서 순서대로 호출
- 훅(Hook)
- 템플릿 메서드 패턴에서 선택적으로 재정의할 수 있는 기본 구현을 제공하는 메서드로 추상 메서드가 아닌 일반 메서드로 구현
- 반환 타입을 boolean으로 구현하여 부모의 템플릿 메서드의 순서를 제어하는 경우에도 사용
public abstract class Template {
// 템플릿 메서드
public final void template() {
start(); // 변하지 않는 공통 로직
if(hook()) {
call();
}
call2();
end(); // 변하지 않는 공통 로직
}
private void start() {
System.out.println("start");
}
private void end() {
System.out.println("end");
}
// 하위 클래스에서 구현 - 추상 메서드
protected abstract void call();
protected abstract void call2();
// 선택적으로 오버라이드 가능한 훅 메서드
protected boolean hook() {
return false;
}
}
// 구현
class ConcreteA extends Template {
@Override
protected void call() {
System.out.println("A call");
}
@Override
protected void call2() {
System.out.println("A call2");
}
}
class ConcreteB extends Template {
@Override
protected void call() {
System.out.println("B call");
}
@Override
protected void call2() {
System.out.println("B call2");
}
@Override
protected boolean hook() {
return true;
}
}
public class TemplateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Template templateA = new ConcreteA();
System.out.println("Executing ConcreteA:");
templateA.template();
Template templateB = new ConcreteB();
System.out.println("Executing ConcreteB:");
templateB.template();
}
}
이렇게 하면 공통 로직에 대한 코드 중복 제거가 가능하고 재사용할 수 있으며 확장성이 용이하다는 장점이 있다.
하지만 상속을 사용하므로 상위 클래스와 하위 클래스 간에 강하게 결합되어 부모 클래스에 변경이 있을 시 자식 클래스에 영향을 미친다.
또한 부모 클래스의 기능을 사용하지도 않는데 부모 클래스에 의존적이라는 단점이 있다.
'디자인 패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Design Pattern] 정적 팩토리 메서드 패턴 (0) | 2025.04.14 |
|---|---|
| [Design Pattern] 데코레이터 패턴 (0) | 2024.12.26 |
| [Design Pattern] 프록시 패턴 (0) | 2024.12.26 |
| [Design Pattern] 템플릿 콜백 패턴 (0) | 2024.12.25 |
| [Design Pattern] 전략 패턴 (0) | 2024.12.25 |


